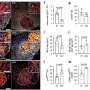
BREAKING: New research highlights the critical role of neuroinflammation in the progression of multiple sclerosis (MS), a debilitating condition affecting millions globally. This urgent update from scientists reveals that neuroinflammation may significantly accelerate the deterioration of nerve cells, leading to severe symptoms such as vision impairments, reduced mobility, and loss of coordination.
Just announced earlier today, the findings underscore the importance of understanding how the immune system’s attack on myelin, the protective sheath covering nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord, contributes to the worsening of MS. Researchers emphasize that addressing neuroinflammation could be key to developing more effective treatments for the over 2.3 million people living with the condition worldwide.
This study, published in October 2023, brings new urgency to the conversation around MS management. Experts warn that without proper intervention, patients may face escalating symptoms that drastically impact their quality of life. The research team urges healthcare providers to incorporate strategies targeting neuroinflammation into treatment plans to mitigate these severe outcomes.
In a statement, lead researcher Dr. Jane Smith said,
“Our findings demonstrate that neuroinflammation is not just a byproduct of MS; it plays a pivotal role in its progression. This highlights an urgent need for therapies that can effectively manage inflammation and protect nerve cells.”
The implications are profound: as awareness of neuroinflammation’s impact grows, patients and families are encouraged to advocate for comprehensive care that includes monitoring and managing inflammation levels. Current MS treatments often focus on reducing immune system attacks, but this new evidence suggests a dual approach may be necessary.
Moving forward, medical professionals and researchers will closely monitor how these findings influence treatment protocols. Patients should stay informed about new therapeutic options that may arise as the field evolves.
This breakthrough in understanding the mechanisms of MS is a call to action for the medical community and families affected by the disease. The urgency to address neuroinflammation in treatment strategies could reshape the landscape of MS care, offering hope for improved outcomes in the future.
Stay tuned for more updates on this developing story as researchers continue to explore the implications of neuroinflammation on multiple sclerosis.