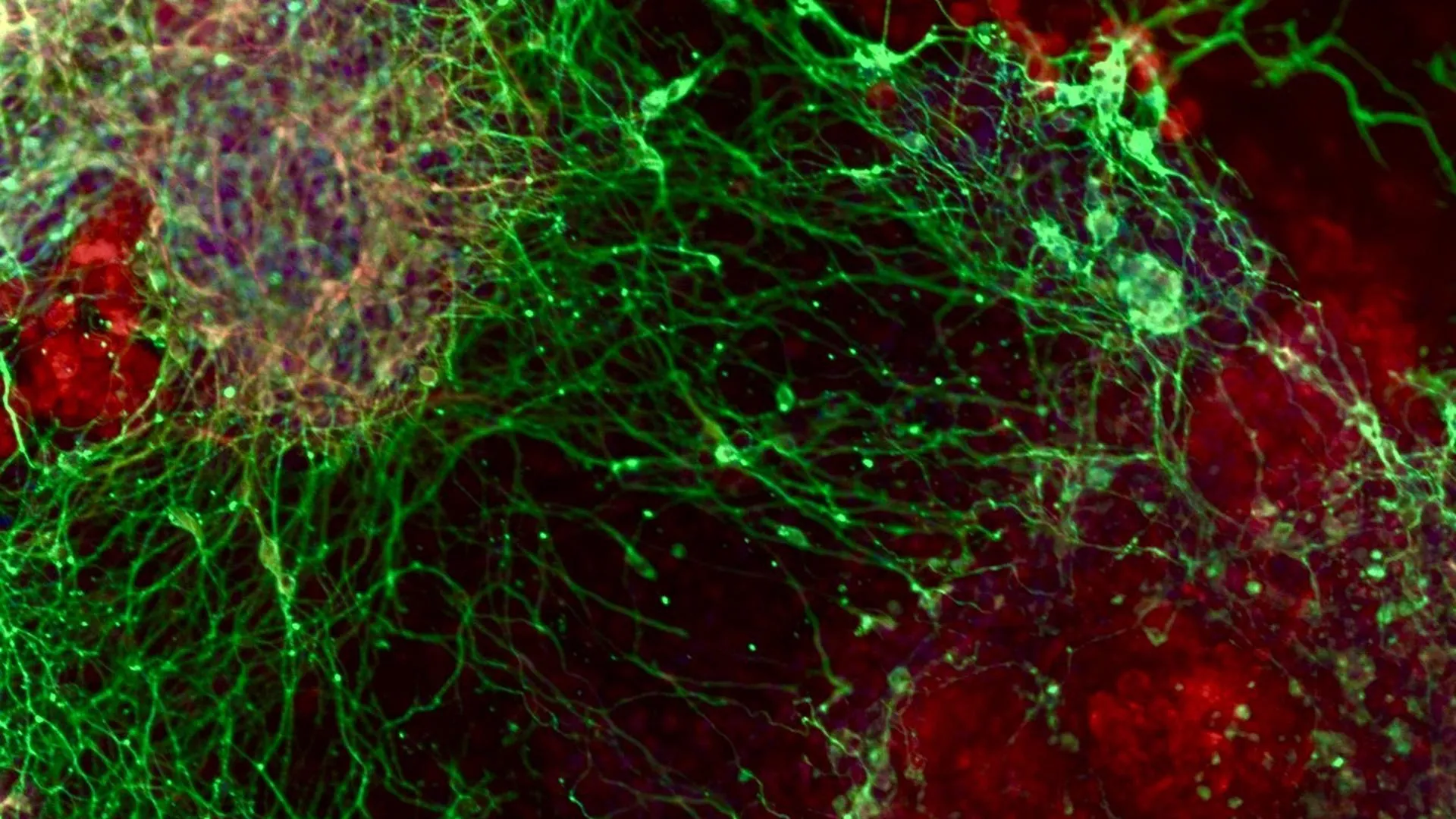
URGENT UPDATE: A groundbreaking study published on January 5, 2026, reveals critical insights into how embryonic stem cells transform into brain cells, identifying 331 genes crucial for this process. Conducted by researchers from The Hebrew University of Jerusalem and INSERM in France, this research sheds light on genetic factors linked to neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism and developmental delays.
Utilizing advanced CRISPR gene-editing technology, the team systematically disabled nearly 20,000 genes to determine which ones are vital for normal brain development. Prof. Sagiv Shifman, leading the research, stated, “By tracking the differentiation of embryonic stem cells into neural cells, we created a map of genes essential for brain development.” This urgent investigation not only maps gene functions but also identifies potential genetic causes of developmental impairments in children.
Among the key discoveries is the gene PEDS1, linked to a newly recognized neurodevelopmental disorder. When PEDS1 malfunctions, it hampers brain growth and nerve cell formation, leading to reduced brain size and significant developmental delays. Genetic testing of two unrelated families showed that children with severe developmental symptoms carried rare mutations in PEDS1, underscoring the gene’s importance.
The study’s implications are immediate. Understanding PEDS1’s role can enhance genetic diagnostics and counseling for families grappling with developmental disorders. It also opens avenues for targeted treatments, potentially revolutionizing approaches to neurodevelopmental conditions.
In addition to identifying PEDS1, the research provides an “essentiality map” of genes required during different stages of development. This map distinguishes genetic mechanisms associated with autism from those linked to general developmental delays, indicating that early changes in brain development can lead to various symptoms.
Prof. Sagiv Shifman emphasized, “Our findings not only help clarify the genetic underpinnings of neurodevelopmental disorders but also serve the scientific community through an open database that allows ongoing research.” The database, launched alongside the study, enables global researchers to explore and build upon these findings.
Supported by the Israel Science Foundation, this ambitious study represents a significant step forward in understanding the complexities of brain development. The implications for families affected by neurodevelopmental disorders are profound, offering hope for improved diagnosis and treatment options.
As this research continues to unfold, the scientific community is urged to engage with the open data to further explore the identified genes and their potential impact on neurodevelopmental disorders. The urgency of these discoveries cannot be overstated, as further insights could lead to groundbreaking advancements in understanding and treating conditions that affect countless children worldwide.
Stay tuned for more updates as this story develops, and share this important research to raise awareness about the genetic factors influencing brain development and disorders.