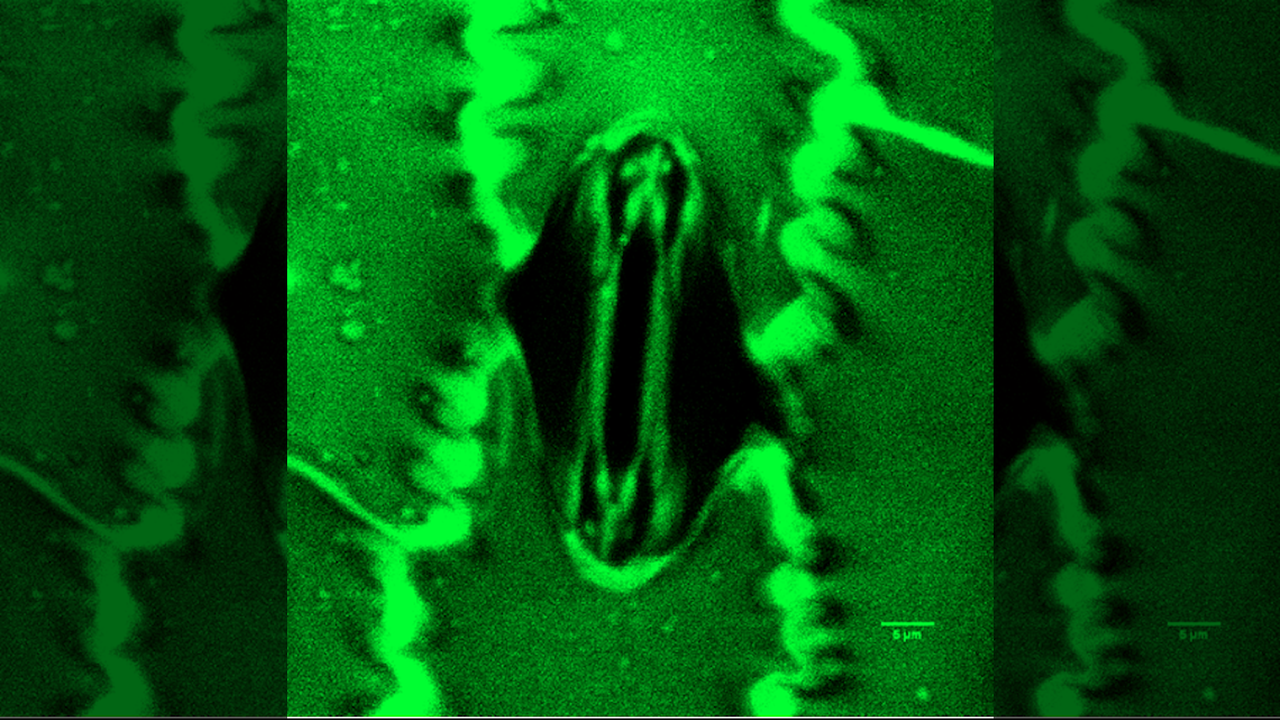
Recent research has uncovered potential mechanisms responsible for specific genetic changes that may lead to cancer. By examining the DNA of fission yeast, scientists have identified how these alterations can contribute to the chaos often seen in cancer-linked chromosomes. This study sheds light on previously hidden triggers associated with disease onset.
The investigation into fission yeast, a model organism that shares similarities with human cells, has provided valuable insights. Researchers have noted that changes in gene expression can significantly affect cellular behavior. By understanding these alterations, scientists aim to clarify the processes that underlie the development of various diseases, including cancer.
Understanding Genetic Changes in Fission Yeast
Fission yeast is particularly useful in scientific research due to its simplicity and genetic similarity to human cells. This study highlights how specific gene modifications can disrupt cellular functions, potentially leading to tumor development. The researchers focused on identifying the triggers that initiate these genetic changes, which remain poorly understood.
The findings suggest that certain environmental factors or cellular stressors may play a crucial role in initiating genetic alterations. By pinpointing these triggers, the study opens new avenues for research into preventative measures and therapeutic interventions for diseases linked to genetic chaos.
Implications for Cancer Research
The implications of this research extend beyond basic science. Understanding the mechanisms behind genetic changes could lead to the development of targeted therapies aimed at preventing or treating cancer. As the scientific community continues to explore the connections between genetics and disease, studies like this one provide foundational knowledge that can inform future research and clinical practices.
The research was conducted by a team of scientists who emphasized the importance of using model organisms to uncover complex biological processes. Their work not only contributes to the existing body of knowledge but also sets the stage for further investigations into the genetic basis of cancer.
As researchers continue to delve into the intricacies of genetic changes, the hope is that this newfound understanding will ultimately lead to improved health outcomes for individuals at risk of developing cancer. The study serves as a reminder of the potential that lies within the microscopic worlds of organisms like fission yeast, which can unlock secrets vital for human health.