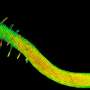
An international team of researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, has uncovered a mechanism that drives the twisted growth patterns observed in various plant organs. This discovery, published on March 15, 2024, highlights how plants utilize twisting as a strategy to navigate their environments effectively.
Twisted growth is not only a fascinating aspect of plant biology but also a functional adaptation that allows plants to master obstacles. For example, morning glories can spiral around fence posts, while grape vines corkscrew through arbors. These adaptations enable plants to optimize their access to sunlight and support for growth.
Understanding the Mechanism
The research team, led by Dr. Andrew Jones, focused on the cellular processes that contribute to this twisting behavior. They discovered that plant cells can expand unevenly, allowing the organs to twist in specific directions. This uneven growth is influenced by both genetic factors and environmental conditions, such as light exposure and physical barriers like rocks.
The study employed advanced imaging techniques to observe the growth patterns of various plants. The team found that roots, for instance, often “do the twist,” skewing to the left or right to avoid obstacles. This behavior is crucial for ensuring that roots find water and nutrients in challenging soil conditions.
According to Dr. Jones, “Understanding how plants adapt their growth patterns not only sheds light on their survival strategies but may also inform agricultural practices. By manipulating these mechanisms, we could potentially enhance crop resilience in various environments.”
Implications for Agriculture and Ecology
The implications of this research extend beyond plant biology. The ability to understand and possibly influence twisted growth patterns could have significant impacts on agriculture and ecological management. For instance, crops that can better navigate their environment might yield higher productivity and require fewer resources.
This discovery also raises important questions about how plants will adapt to changing environmental conditions, such as urban development and climate change. As human activities continue to reshape landscapes, understanding plant adaptability will be crucial for conservation efforts.
In summary, the recent findings from the University of California, Berkeley, provide a deeper insight into the adaptive mechanisms of plants. With further research, these insights could lead to innovative strategies for enhancing agricultural practices while fostering ecological sustainability.