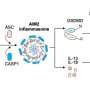
A team of researchers at Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) has made significant strides in understanding the immune response during infections caused by the mpox virus (MPXV). Their study reveals that the AIM2 protein acts as a crucial sensor that detects the viral DNA of MPXV, initiating a severe inflammatory response that may exacerbate the disease.
Understanding the immune system’s overreaction is vital as it can lead to serious health complications. The researchers found that when MPXV infects the body, the AIM2 protein identifies the presence of the virus’s DNA. This detection triggers a potent immune response characterized by inflammation, which, while intended to combat the virus, can contribute to the overall severity of the infection.
Insights into Immune Mechanisms
The research emphasizes the double-edged nature of the immune response. While inflammation is a natural defense mechanism, excessive inflammation can be detrimental. The study highlights how AIM2’s activation can lead to an overwhelming inflammatory response, potentially resulting in tissue damage and severe symptoms in infected individuals.
Researchers utilized advanced techniques to observe the interactions between AIM2 and MPXV. The findings suggest that targeting this protein might offer new therapeutic avenues to manage mpox infections more effectively. By modulating the AIM2 pathway, health professionals could potentially reduce the severity of inflammation and improve patient outcomes.
Implications for Future Research
This discovery opens the door for further investigations into the treatment of mpox and similar viral infections. As the global community continues to grapple with emerging infectious diseases, understanding the mechanisms behind immune responses becomes increasingly important.
The study conducted by the UNIST team is part of a broader effort to unravel how the immune system interacts with various pathogens. With mpox cases on the rise, insights gained from this research could play a pivotal role in developing effective antiviral therapies and vaccines.
The findings of this study underscore the importance of ongoing research in the field of immunology. As scientists continue to explore the complexities of the immune response, breakthroughs like this one will be essential in guiding public health strategies and improving treatment protocols for viral infections.