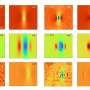
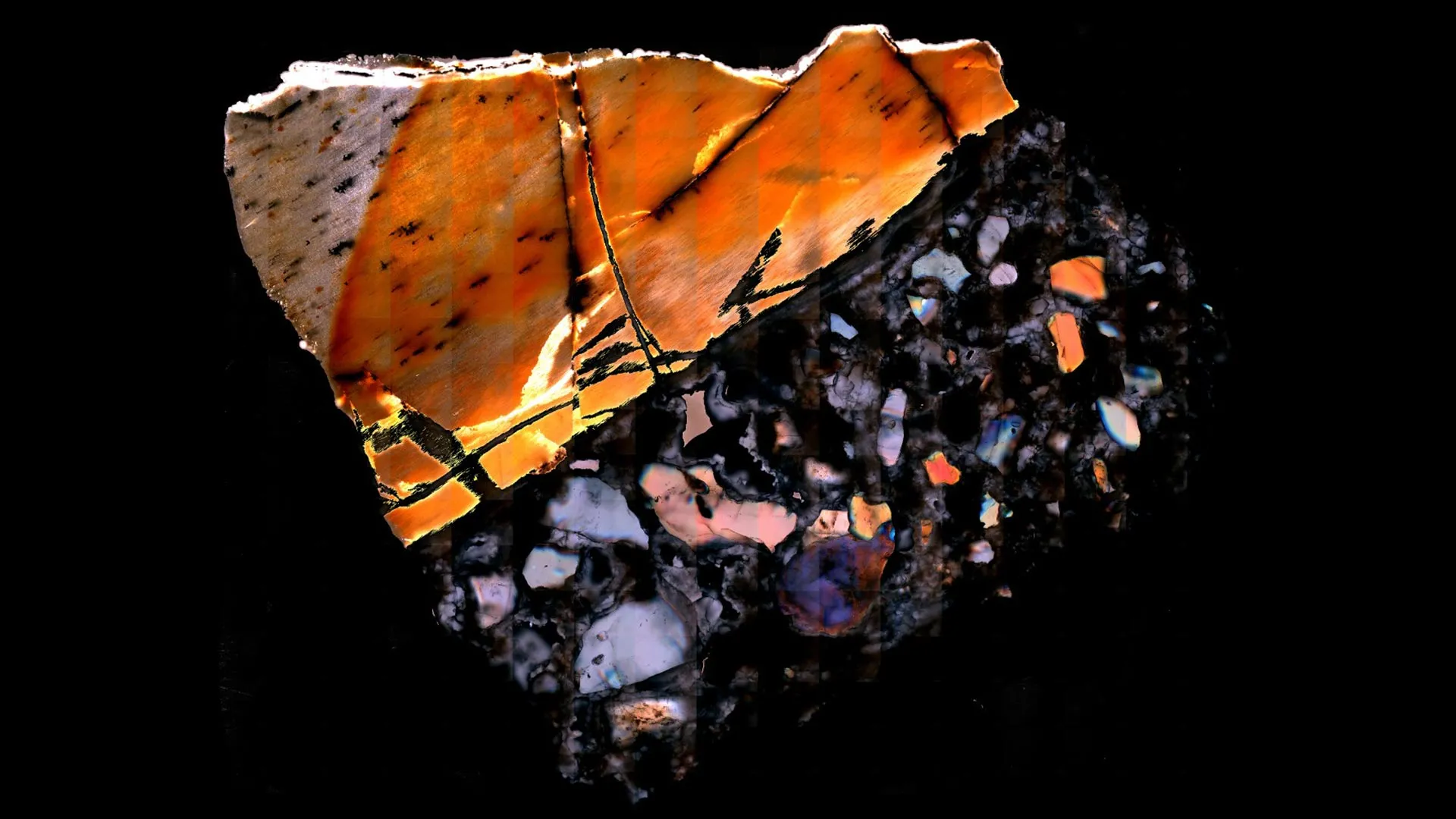
Researchers at the University of Ferrara in Italy have achieved a significant breakthrough by successfully creating a ‘lump soliton’. This innovative packet of light waves is capable of traveling through three-dimensional space while maintaining its shape, even when interacting with other solitons. This development marks the first time such resilient 3D solitons have been produced in a laboratory setting.
The creation of these solitons has implications beyond theoretical physics. Traditionally, solitons are known for their stability in one or two dimensions, but the introduction of a three-dimensional variant opens up new possibilities for applications in fields such as telecommunications and quantum computing. The researchers have noted that these solitons can interact without distortion, which could enhance the efficiency of data transmission in optical fibers.
Understanding the Significance of 3D Solitons
The discovery of stable 3D solitons is a remarkable advancement in the study of wave phenomena. According to the lead researcher, Professor Marco G. De Luca, this work not only enriches the understanding of light wave dynamics but also paves the way for practical applications.
“The ability to maintain integrity while interacting with other solitons is a game-changer for the field of photonics,”
stated Professor De Luca.
This research is part of a broader effort within the scientific community to explore new ways in which light can be harnessed for advanced technologies. The team at the University of Ferrara has utilized advanced optical techniques to generate these solitons, employing cutting-edge equipment to manipulate light in novel ways. The experiments involved intricate setups that allowed precise control over the light waves, leading to the successful formation of the lump solitons.
The findings were published in a leading scientific journal in March 2024, receiving attention for their potential to revolutionize how information is transmitted over long distances. As the world increasingly relies on high-speed internet and efficient data transfer, the implications of this research could be substantial.
Future Implications and Applications
The implications of creating resilient 3D solitons extend into various sectors. Telecommunications companies may find potential in using these solitons to develop faster and more reliable communication networks. Moreover, the integration of 3D solitons could foster advancements in quantum computing, where the manipulation of light plays a crucial role in the processing of information.
In addition to practical applications, this discovery encourages further investigation into the fundamental properties of light and wave interactions. Scientists are optimistic that ongoing research will lead to additional breakthroughs, potentially uncovering new physical phenomena related to soliton dynamics.
As the scientific community continues to explore the properties and applications of these newly developed solitons, the work done by the team at the University of Ferrara stands as a testament to the innovative spirit of modern physics. The future of light-based technologies may very well be illuminated by these resilient wave packets, shaping the way data is transmitted across the globe.