Researchers at the University of Bonn have developed a groundbreaking method that utilizes artificial intelligence to generate lifelike 3D models of plant leaves, significantly advancing the field of plant phenotyping. Published in the journal Plant Phenomics on June 16, 2025, this study addresses longstanding challenges in accurately estimating leaf traits, which traditionally require extensive manual data collection.
The method employs synthetic “leaf point clouds” to enhance the accuracy and scalability of trait estimation in crop research. Traditional plant phenotyping techniques often rely on 2D imaging, which struggles to capture the complexities of leaf curvature and geometry. Moreover, existing 3D approaches are hindered by the scarcity of labeled data necessary for effective training. This new system aims to automate the generation of high-quality, labeled 3D data, thereby streamlining the process of phenotyping.
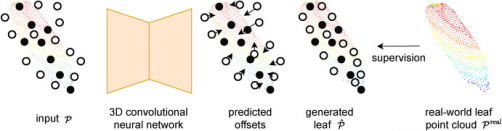
Gianmarco Roggiolani and his research team tackled these limitations by training a 3D convolutional neural network. This model learns to create realistic leaf structures based on skeletonized representations derived from real leaves. By analyzing datasets from sugar beet, maize, and tomato plants, the researchers extracted the essential “skeleton” elements of each leaf, including the petiole and main axes. They then transformed these skeletons into dense point clouds using a Gaussian mixture model.
The neural network, designed as a 3D U-Net architecture, predicts offsets for each point to accurately reconstruct the complete leaf shape while preserving its structural traits. To ensure high fidelity, the researchers combined reconstruction and distribution-based loss functions, allowing the generated leaves to align closely with the geometric and statistical properties of actual data.
In validation tests, the synthetic dataset was compared against existing generative approaches and real agricultural data using metrics such as the Fréchet Inception Distance (FID) and precision-recall F-scores. Results indicated that the generated leaves exhibited a high degree of similarity to real leaves, surpassing alternative datasets created by agricultural simulation software.
The implications of this research extend beyond data generation. When the synthetic data were utilized to refine existing leaf trait estimation algorithms—such as polynomial fitting and principal component analysis—the accuracy and precision of predictions improved significantly. Tests conducted on the BonnBeetClouds3D and Pheno4D datasets revealed that models trained with this new synthetic data estimated real leaf dimensions with greater accuracy and reduced error variance.
One of the standout features of this method is its ability to produce diverse leaf shapes based on user-defined traits. This flexibility facilitates robust benchmarking and model development without the need for costly manual labeling, potentially revolutionizing the way researchers approach plant phenotyping.
This study marks a crucial step toward automating 3D plant phenotyping and alleviating the bottleneck created by limited labeled data. By enabling the generation of realistic data based on real plant structures, the approach lays a strong foundation for the development and enhancement of trait estimation algorithms within agriculture.
Looking ahead, the research team plans to expand this methodology to accommodate more complex leaf morphologies and integrate it with plant growth models. The vision includes creating open-access libraries of synthetic, biologically accurate plant datasets, which would support research in sustainable agriculture, robotic phenotyping, and crop improvement in the face of climate challenges.
The study received partial funding from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), under Germany’s Excellence Strategy, EXC-2070 – 390732324 – PhenoRob, highlighting the collaborative efforts to advance plant science through innovative technology.