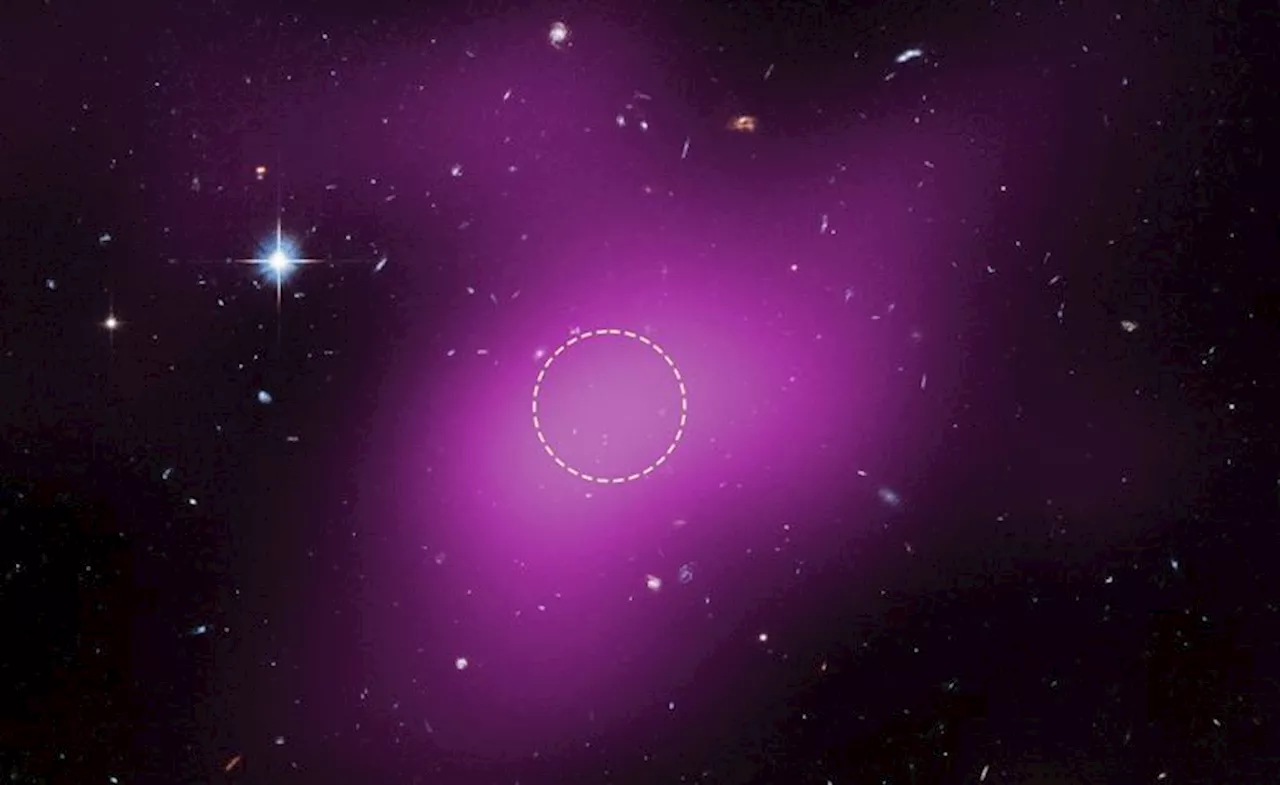
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has made a remarkable discovery, identifying a new cloud of gas and dark matter that may represent a “failed” galaxy. This newly observed object, informally dubbed Cloud-9, is located near the spiral galaxy Messier 94, approximately 14 million light-years from Earth. Astronomers believe this finding challenges conventional theories about galaxy formation.
Principal investigator Alejandro Benitez-Llambay from the University of Milano-Bicocca stated, “This is a tale of a failed galaxy. The absence of stars is exactly what proves the theory right. It tells us that we have found a primordial object that hasn’t yet — or may never — lit up the cosmos with starlight.”
The research highlights that Cloud-9 is nearly invisible in optical light due to its lack of stars. Observations using Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys revealed a faint, ghostly concentration of gas, which is primarily composed of dark matter. This combination provides strong evidence for an object long theorized by scientists, known as a Reionization-Limited H I Cloud (RELHIC).
Significance of Cloud-9
According to NASA, in the early universe, certain dark matter halos were capable of gathering gas but failed to initiate star formation. Such conditions have led to the existence of rare, starless relics like Cloud-9, which have remained largely undetected until now. The identification of this object confirms a crucial prediction of cosmological models and offers a unique glimpse into the processes that shape galaxies—specifically, how some fail to form altogether.
The discovery not only challenges existing paradigms in astronomy but also enhances understanding of the universe’s evolution. The findings suggest that these primordial clouds could provide insights into the conditions that existed shortly after the Big Bang.
Astronomers are excited about the implications of this discovery, as it could lead to further exploration of the early universe and its unobservable components. Cloud-9 serves as a vivid reminder of the mysteries that still lie beyond our current understanding of the cosmos.
As the Hubble Space Telescope continues to explore the depths of space, scientists anticipate uncovering more about such enigmatic structures. The study of Cloud-9 will likely lead to further research into the nature of dark matter and the conditions that govern galaxy formation. For now, astronomers are on “Cloud-9” with the revelations this failed galaxy brings to light.