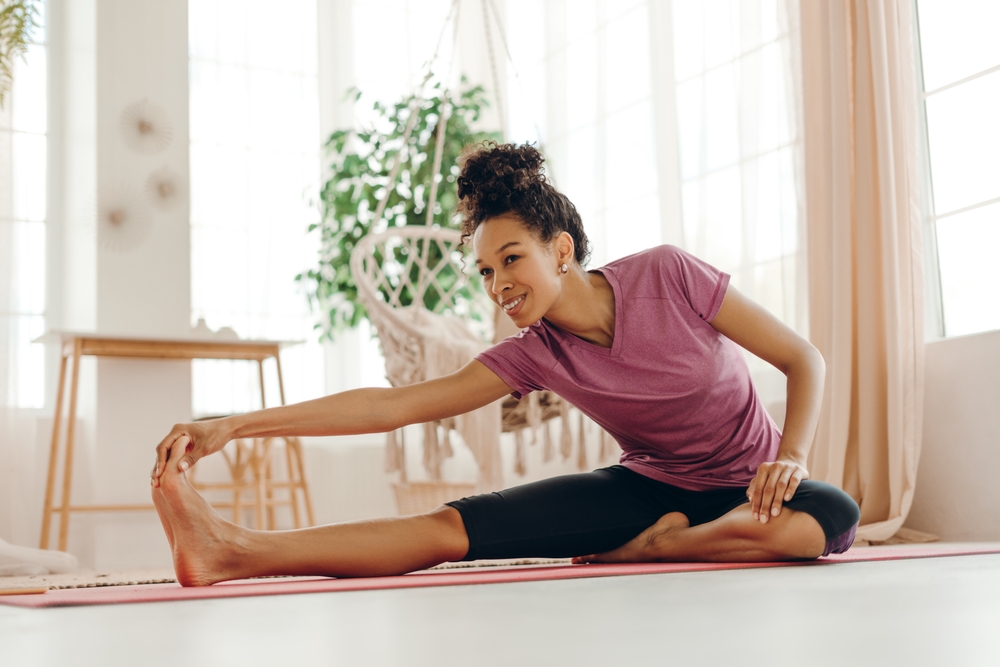
Fascial stretch exercises can significantly reduce discomfort in the shoulders, neck, and lower back by targeting the fascia, a crucial connective tissue in the body. Recent insights into fascia reveal that many unexplained aches stem from fascial adhesions, which can occur due to a variety of lifestyle factors. To address these issues, regular stretching is recommended to maintain the fascia’s flexibility and hydration.
Understanding fascial adhesion is essential for tackling pain. Fascia, primarily composed of water and collagen, envelops muscles, bones, and organs. When the fascia remains hydrated and organized, bodily movements tend to be smooth and efficient. Yet, when it becomes dry, tight, or adheres to itself, it can lead to restricted movement and chronic discomfort.
Several factors contribute to the development of fascial adhesions. Prolonged immobility, particularly in sedentary individuals or those who remain seated for extended periods, causes collagen within the fascia to become sticky, hindering mobility. Additionally, excessive load from weight training or poor posture can induce stress on the fascia, resulting in micro-tears. Inactivity following an injury can also lead to stiffness and fascial adhesion, while aging naturally reduces the moisture content of fascia, making it more fibrotic.
The benefits of incorporating fascial stretching into a regular routine are noteworthy. This practice can enhance flexibility and range of motion, promote metabolic regulation, improve proprioception, and reduce injury risk. Stretching helps to keep the fascia elastic, enabling it to absorb impacts effectively and protect muscles and joints during daily activities.
Benefits of Fascial Stretching
1. **Improved Flexibility and Range of Motion**: Regular stretching enhances joint flexibility and reduces stiffness and discomfort.
2. **Promotes Metabolism and Regulatory Function**: Stretching the fascia can positively influence metabolic and endocrine functions on a cellular level.
3. **Enhanced Proprioception**: Improved motor coordination can lead to better stability and a reduced risk of falls.
4. **Reduced Risk of Injury**: Elastic fascia acts as a protective barrier for muscles and joints, absorbing impacts during movement.
The human body consists of various interconnected fascial lines, with the superficial dorsal line being particularly significant. This line starts at the scalp and traverses the neck, back, buttocks, and extends to the thighs, calves, and soles of the feet. Engaging in fascial stretches targeting this line can be particularly beneficial.
Incorporating these exercises into daily routines can make a substantial difference in overall well-being. Individuals suffering from discomfort in the shoulders, neck, and lower back are encouraged to explore these stretching methods as a proactive approach to enhance their physical health and quality of life.