Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, have unveiled a groundbreaking method to produce hydrogen from impure water sources, including seawater and industrial wastewater. This development promises to enhance the reliability and scalability of hydrogen production, addressing significant challenges in the transition to sustainable energy.
The new technique utilizes a specialized “smart gate” system that effectively separates hydrogen from other elements found in impure water. This innovative approach not only simplifies the hydrogen generation process but also reduces costs and energy consumption, making it a viable option for large-scale applications. As global demand for clean energy sources increases, this research holds the potential to revolutionize how hydrogen is produced.
Transforming Water Sources into Energy Solutions
Hydrogen is widely recognized as a clean fuel alternative, especially in sectors like transportation and energy storage. However, traditional methods of hydrogen production often rely on pure water sources, which can be limited and expensive. The method developed by the Berkeley researchers changes this paradigm by effectively utilizing seawater, which is abundant and accessible.
According to the research team, the smart gate system can efficiently filter out impurities while extracting hydrogen. This capability is crucial, considering that many regions worldwide face water scarcity. By tapping into seawater and industrial wastewater, this technology can support hydrogen production without depleting freshwater resources.
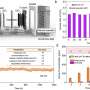
The researchers conducted extensive tests to demonstrate the effectiveness of their method. They reported that the smart gate system achieved a hydrogen production efficiency of over 80% when using seawater. This level of efficiency is a significant milestone, as it meets the critical requirements for commercial viability.
A Step Towards Sustainable Energy Infrastructure
The implications of this research extend beyond just hydrogen production. As countries strive to meet their climate goals, finding sustainable energy solutions is paramount. The ability to generate hydrogen from seawater could lead to the establishment of new hydrogen infrastructure, particularly in coastal regions where seawater is readily available.
Hydrogen is expected to play a pivotal role in achieving carbon neutrality. By adopting this innovative method, industries can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels, thereby lowering greenhouse gas emissions. The researchers envision this technology being implemented in various sectors, including transportation, manufacturing, and power generation.
The findings of this research were published in a leading scientific journal in late 2023, garnering attention from environmental and energy sectors alike. The development of the smart gate system signifies a crucial step toward a more sustainable and resilient energy future.
In conclusion, the advancements made by the team at the University of California, Berkeley, represent a significant breakthrough in hydrogen production. By leveraging abundant water sources such as seawater and industrial wastewater, this method not only addresses current energy challenges but also paves the way for a more sustainable approach to meeting global energy demands.