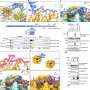
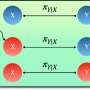
Ribosomes, the essential protein-producing structures within cells, trigger emergency stress responses when they encounter disruptions during protein synthesis. This discovery was detailed in a study published in April 2023 by researchers at the University of California, highlighting the critical role of ribosomes in maintaining cellular health.
Ribosomes operate by binding to messenger RNA (mRNA) and translating genetic instructions into proteins. They move along the mRNA strand, linking specific amino acids to build proteins vital for numerous cellular functions. When ribosomes collide—either due to a backlog of mRNA or errors in the genetic code—cells initiate a series of defensive measures to prevent damage and maintain homeostasis.
Mechanism of Stress Response
The study reveals that when ribosomes malfunction, cells activate pathways that help mitigate potential damage. This response includes the production of stress granules, which are cellular structures that store and regulate proteins and RNA during stressful conditions. By creating these granules, cells can effectively manage the resources needed to rectify the ribosomal malfunctions.
According to the research, this mechanism is not merely a reactive measure; it plays a crucial role in the overall health and longevity of cells. The stress response ensures that even when ribosomes encounter obstacles, the cellular machinery can adapt and continue functioning efficiently.
Implications for Health and Disease
Understanding how ribosomes interact with mRNA and respond to stress has significant implications for various fields, including medicine and biotechnology. Disruptions in ribosomal function are linked to numerous diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. By gaining insights into these stress responses, researchers may develop new therapeutic strategies aimed at enhancing cellular resilience and combating disease.
The findings underscore the importance of ribosomes beyond their conventional role in protein synthesis. They serve as vital sensors of cellular stress, enabling cells to navigate challenges effectively. As research continues to unfold, the potential for applications in health and disease management remains vast.
This study not only enriches our understanding of cellular biology but also paves the way for future innovations in medical research, potentially leading to breakthroughs in treatments for conditions associated with ribosomal dysfunction.