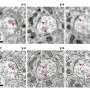
An international team of researchers, spearheaded by the Francis Crick Institute in London and collaborating with the Paul Scherrer Institute in Switzerland, has introduced a groundbreaking imaging protocol. This new method enables detailed visualization of cellular connections within the mouse brain, marking a significant advancement in neuroscience research. The findings, published in the journal Nature Methods, showcase the innovative combination of X-ray imaging with specialized radiation-resistant materials sourced from the aerospace industry.
The study aims to enhance the understanding of brain connectivity, which is crucial for deciphering the complexities of neurological function and disorders. By utilizing advanced X-ray techniques, the researchers provide a clearer view of the intricate web of neurons and synapses that facilitate communication within the brain. This level of detail was previously unattainable using conventional imaging methods.
In their research, the team employed materials known for their durability and resistance to radiation, ensuring that high-resolution images could be captured without compromising the integrity of the samples. This approach not only improves the quality of imaging but also paves the way for future studies into the structural and functional aspects of the brain.
Understanding the precise architecture of brain connections is essential for various fields, including neurobiology and psychology. The insights gained from this research could lead to improved diagnostic techniques and therapeutic strategies for conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, autism, and other neurodevelopmental disorders.
The implications of this work extend beyond basic science; they offer a potential pathway for developing more effective treatments for a range of cognitive and emotional disorders. As researchers continue to explore the complexities of the brain, tools like this new imaging protocol will play a crucial role in advancing neuroscience.
In summary, the innovative imaging protocol developed by the Francis Crick Institute and the Paul Scherrer Institute represents a significant leap forward in our ability to study the brain’s cellular connections. The publication of this research in Nature Methods underscores the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in addressing some of the most pressing challenges in brain research today.