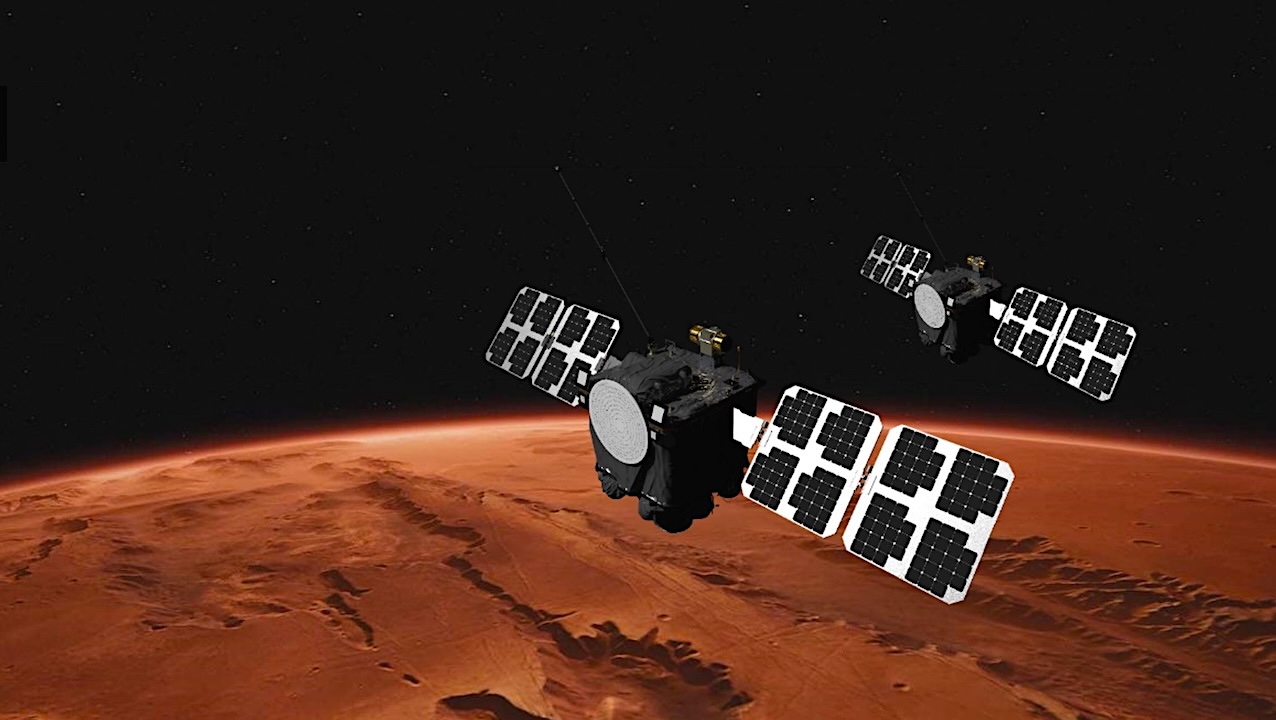
NASA is preparing to launch its first dual-satellite mission to another planet, known as the ESCAPADE mission, which stands for Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers. The launch is scheduled for no earlier than November 9, 2024, from Cape Canaveral, Florida. This innovative mission will utilize two identical satellites managed and operated by the University of California, Berkeley, which will work in tandem to conduct research on the Martian atmosphere.
The ESCAPADE satellites are designed to fly in formation around Mars, allowing scientists to map the planet’s magnetic fields and upper atmosphere. This data is crucial for understanding how solar winds impact Mars and contribute to its atmospheric loss. By studying these dynamics, researchers hope to gain insights into the planet’s potential for past habitability and its current environmental conditions.
Mission Objectives and Significance
The primary objective of the ESCAPADE mission is to explore the interaction between solar wind and Mars’ magnetic field. Current understanding suggests that solar winds strip away the Martian atmosphere, which has implications for the planet’s climate history and potential for supporting life.
The twin satellites will orbit Mars at different altitudes, providing a comprehensive view of the planet’s magnetic environment. This will enable scientists to observe how solar particles affect the Martian atmosphere in real-time. The data collected could advance our knowledge of planetary atmospheres beyond Earth, particularly those of exoplanets.
Collaboration and Future Implications
The collaboration between NASA and the University of California, Berkeley, highlights the increasing role of academic institutions in space exploration. The ESCAPADE mission exemplifies how university-led projects can contribute significantly to national space objectives while fostering educational opportunities for students and researchers.
As the launch date approaches, excitement is building within the scientific community and among space enthusiasts. The mission’s findings could have far-reaching implications, not only for Mars research but also for future human exploration of the planet. Understanding the Martian atmosphere is critical for planning sustainable missions and potential colonization efforts.
In summary, NASA’s ESCAPADE mission represents a significant step in planetary science and exploration. With the launch scheduled for November 9, 2024, the world eagerly awaits the insights that these twin satellites will deliver on Mars’ atmosphere and magnetic field dynamics.