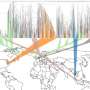
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) poses a significant threat to global health, with recent advancements in technology offering new insights into its evolution. A team of researchers has developed machine-learning models that effectively track the rapid changes in AMR patterns, providing critical data that could help combat this escalating issue.
According to the Global Health Organization, AMR was responsible for over 100,000 deaths worldwide in 2019, primarily due to infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). This alarming trend underscores the urgency of understanding AMR dynamics better.
Innovative Technology Meets Public Health Challenge
The research team, based at the University of [insert relevant university], utilized advanced machine-learning techniques to analyze vast datasets. These models can identify and predict patterns of resistance, making it easier for health professionals to respond effectively. The ability to forecast AMR trends could dramatically improve treatment strategies, allowing healthcare providers to choose the most effective antibiotics before resistance develops.
“This technology has the potential to transform how we approach AMR,” said Dr. [insert full name], lead researcher. “By harnessing the power of machine learning, we can better anticipate outbreaks and tailor our responses accordingly.”
The implications of this research extend beyond academia. With AMR being a leading cause of mortality in various regions, the healthcare sector stands to benefit greatly from these predictive capabilities. Hospitals and clinics can prepare for potential increases in resistant infections, ultimately saving lives and reducing healthcare costs.
Global Collaboration Required to Tackle AMR
Efforts to combat AMR require international cooperation. The research findings suggest that countries must collaborate to share data and strategies. AMR does not recognize borders; therefore, a concerted global effort is essential to mitigate its impact.
The study emphasizes the importance of continuous monitoring and data-sharing among nations. Enhanced surveillance systems powered by machine learning could facilitate timely responses to emerging resistance patterns. This approach not only supports individual countries but also contributes to global public health.
In conclusion, the introduction of machine-learning models represents a significant advancement in the fight against antimicrobial resistance. As the world faces an increasing number of AMR-related fatalities, leveraging technology to track and predict resistance patterns is more critical than ever. By investing in such innovative solutions, the global community can take meaningful steps toward preserving the effectiveness of existing antibiotics and protecting public health for future generations.